Table of Contents
Can you Feel your Liver is healing?
Yes, your liver can heal and regenerate. Liver cells can grow back after being damaged or removed. This is because the liver has the ability to regenerate liver cells. New liver cells grow and multiply at the site of injury or removal. However, liver disease can impact the liver’s ability to heal. Scarring and inflammation can hinder the healing process.
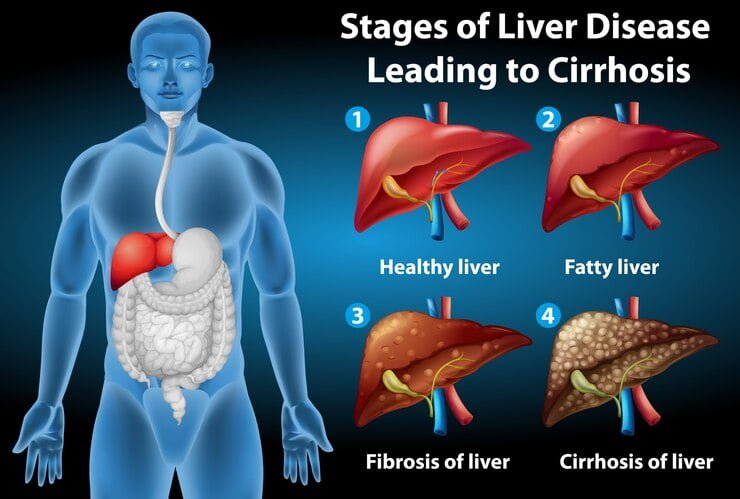
Usually, you cannot physically feel your liver healing during cirrhosis. The healing process in the liver, particularly in cirrhosis, involves the reduction of inflammation and fibrosis (scar tissue) and the regeneration of healthy liver tissue. However, this process usually happens gradually over time and is not something that can be felt through physical sensations such as pain or discomfort.
Understanding the Liver Healing Process:
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including detoxification, metabolism, and nutrient storage. Understanding how the liver heals is essential for anyone looking to support liver health, recover from liver damage, or enhance overall well-being. This guide delves into the liver healing process, the factors affecting it, and actionable steps to promote recovery.
The Role of the Liver in the Body
The liver is the largest internal organ, weighing about 3 pounds, and is responsible for over 500 functions, including:
- Detoxification: The liver filters toxins and waste products from the bloodstream, including drugs, alcohol, and metabolic byproducts. It converts harmful substances into less toxic forms that can be excreted through urine or bile.
- Metabolism: The liver plays a key role in metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It converts glucose into glycogen for storage and regulates blood sugar levels. It also processes lipids and synthesizes cholesterol and proteins necessary for bodily functions.
- Bile Production: The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid that aids in the emulsification and absorption of fats in the intestine. Bile also helps eliminate waste products from the body.
- Nutrient Storage: The liver stores essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12, as well as iron and copper. This storage capacity ensures that the body has access to vital nutrients when needed.
How the Liver Heals
The liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate itself. This healing process occurs through several stages:
- Cellular Regeneration: When liver cells (hepatocytes) are damaged, they have the ability to proliferate and replace lost or damaged cells. This regeneration can begin within days after injury, allowing the liver to restore its mass and functionality.
- Inflammation Reduction: Liver damage often leads to inflammation, which can impede healing. As the liver heals, inflammatory responses diminish, allowing for improved blood flow and cellular function. Anti-inflammatory cytokines and other factors are produced to help resolve inflammation.
- Restoration of Blood Flow: The liver has a unique blood supply, receiving blood from both the hepatic artery and the portal vein. During the healing process, any compromised blood vessels are repaired, ensuring adequate blood flow to deliver nutrients and oxygen, which are crucial for recovery.
- Functional Recovery: Over time, as the liver heals, it regains its ability to perform essential functions, including detoxification, nutrient metabolism, and bile production. Regular monitoring of liver function tests can help track this recovery process.
Factors Affecting the Liver Healing Process
Several factors can influence the effectiveness and speed of liver healing:
- Severity of Damage: The extent of liver damage plays a significant role. Conditions like cirrhosis or advanced fatty liver disease can slow the healing process, as extensive scarring (fibrosis) impairs liver function.
- Age: Younger individuals generally heal more quickly than older adults due to more robust cellular regeneration capabilities. Age-related factors may also contribute to slower healing.
- Overall Health: Pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome can hinder the liver’s recovery. A healthy lifestyle is crucial for promoting optimal liver function.
- Lifestyle Choices: Diet, alcohol consumption, and physical activity greatly impact liver health. Excessive alcohol intake or a high-fat diet can exacerbate liver damage and slow healing.
Tips to Support Liver Healing
1. Adopt a Healthy Diet:
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can help combat oxidative stress and support detoxification processes.
2. Stay Hydrated:
- Aim to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water daily. Hydration aids the liver in flushing out toxins and supports overall metabolic processes.
3. Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Reducing or eliminating alcohol intake can significantly benefit liver health. Alcohol can cause inflammation and damage liver cells, hindering the healing process.
4. Exercise Regularly:
Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week. Exercise improves circulation, helps maintain a healthy weight, and supports overall metabolic health.
5. Avoid Toxins:
- Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals. Opt for organic produce when possible and use natural cleaning products to reduce chemical exposure.
6. Consider Supplements:
- Some supplements, such as milk thistle (silymarin) and turmeric (curcumin), are believed to support liver health. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements to ensure safety and appropriateness.
7. Get Regular Check-ups:
- Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help monitor liver function through blood tests. Early detection of potential issues allows for timely intervention.
8. Manage Stress:
- Chronic stress can negatively impact liver health. Incorporate stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into your daily routine.
Understanding the liver healing process is essential for anyone looking to improve their liver health or recover from damage. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying informed about liver health, and implementing supportive strategies, you can enhance your liver’s healing capacity and promote overall well-being. Remember, the liver’s remarkable ability to regenerate means that with the right care and attention, you can help your liver thrive.
- Key Takeaway: Supporting liver healing involves a combination of a nutritious diet, regular exercise, hydration, and healthy lifestyle choices. Prioritizing liver health can lead to improved function and overall well-being, empowering you to live a healthier life.
Here are some important points to consider about question Can you Feel your Liver is healing?:
Important Points for Can you Feel your Liver is healing
1. Nature of Cirrhosis:
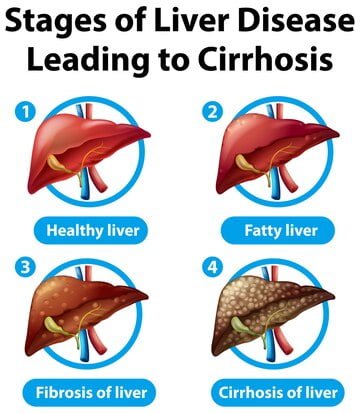
Cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease characterized by the progressive scarring (fibrosis) of liver tissue. This damage disrupts the liver’s normal structure and function, leading to various health complications. Understanding cirrhosis is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Cirrhosis is characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue in the liver due to ongoing injury or damage. The ability of the liver to heal depends on various factors such as the underlying cause of cirrhosis, the extent of liver damage, and the effectiveness of treatment. Read More
Inflammation:
In cirrhosis, ongoing damage to the liver leads to chronic inflammation. Treatment strategies aim to reduce inflammation by addressing underlying causes such as alcoholism, viral hepatitis, or fatty liver disease.
Fibrosis:
Scar tissue (fibrosis) forms as a natural healing response in response to chronic inflammation. Over time, if the underlying cause is controlled, inflammation may decrease, and the process of fibrosis may slow or even reverse.
2. Resolve inflammation:
Treatment and lifestyle changes aimed at addressing the underlying cause of cirrhosis (eg, avoiding alcohol, treating hepatitis infection) can help reduce inflammation in the liver. are As inflammation is reduced, it can help improve liver function over time.
Regeneration of healthy liver tissue:
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate healthy tissue. In cases where the underlying cause of cirrhosis is controlled or eliminated, this regeneration can gradually replace the scar tissue with healthy liver cells. However, this process is slow and may not completely reverse cirrhosis in advanced stages.
Factors Affecting Regeneration:
Factors such as severity of cirrhosis, extent of scar tissue, underlying liver disease, and individual health can affect the ability of the liver to regenerate. Recurrence is more likely when the cause of cirrhosis is successfully treated and further damage is prevented.
3. Symptoms and Feedback:
People with cirrhosis may experience improvement in symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, and fluid retention (skin) as their liver function improves. However, these improvements are usually assessed by clinical tests and monitoring and not by direct visualization of liver healing.
Relief of symptoms:
As inflammation subsides and liver function improves, people with cirrhosis experience a reduction in symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), itching and stomach upset. may be encountered.
4. Monitoring and Medical Guidance:
It is very important for people with cirrhosis to receive regular medical monitoring and follow the treatment plans prescribed by the health care providers. This ensures that any improvement in liver function can be detected early and managed effectively.
In summary, while the liver may undergo a healing process in cirrhosis, this is usually not something that can be directly felt or felt. Monitoring of liver function through clinical tests is important to evaluate treatment progress and overall liver health.
Medical Monitoring:
Regular medical examinations are necessary to monitor liver function and assess the progression of cirrhosis. This includes monitoring for complications such as portal hypertension (high pressure in the portal vein system), varices, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy.
Treatment Strategy:
Depending on the underlying cause and stage of cirrhosis, treatment may include lifestyle changes (eg, diet, exercise), medications to manage symptoms or slow the progression of the disease, and include interventions to prevent complications.
4.Liver Transplantation
End-Stage Cirrhosis:
In cases where cirrhosis has progressed to end-stage liver disease with liver failure and complications that cannot be effectively managed, a liver transplant may be necessary. Liver transplantation offers the best chance of long-term survival and improved quality of life in these conditions.
Conclusion
Finally, while the liver can undergo a healing process in cirrhosis, this healing is a complex and gradual process that is primarily monitored by clinical assessment rather than directly experienced by the individual. Effective management, timely intervention, and addressing underlying causes are critical in supporting liver health and potentially improving outcomes for people with cirrhosis. Regular medical care and adherence to treatment plans are essential components of effectively managing cirrhosis. Read more about health
FAQ: Can You Feel Your Liver Healing?
1. Can I physically feel my liver healing?
While you may not feel the actual healing process, improvements in your overall health can indicate that your liver is recovering. Symptoms such as increased energy, better digestion, and reduced discomfort may suggest positive changes.
2. What symptoms might indicate that my liver is healing?
Signs of liver healing may include reduced fatigue, improved mood, better appetite, decreased jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and less swelling in the abdomen or legs.
3. How long does it take for the liver to heal?
The healing time varies based on the severity of damage, underlying conditions, and lifestyle changes. Mild liver damage may show improvement within weeks to months, while more severe damage may take longer.
4. What lifestyle changes can support liver healing?
Adopting a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, avoiding alcohol, and managing stress can significantly support the liver’s healing process.
5. Can I feel pain or discomfort during the healing process?
Some individuals may experience discomfort or mild pain as the liver recovers, especially if there’s inflammation. However, persistent pain should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
6. Are there any tests to monitor liver healing?
Yes, healthcare providers can monitor liver function through blood tests that measure liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and other markers of liver health.
7. How can I tell if my liver is not healing?
If symptoms persist or worsen, such as ongoing fatigue, jaundice, or abdominal swelling, it may indicate that the liver is not healing properly. Consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
8. Do I need regular check-ups during the healing process?
Yes, regular check-ups are important to monitor liver function, assess healing progress, and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
9. Can supplements help with liver healing?
Some supplements, like milk thistle and turmeric, are believed to support liver health. However, always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
10. What should I do if I have concerns about my liver health?
If you have concerns about your liver health or healing process, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and personalized recommendations.